- Home
-
![]()
 You are here: Home » Blogs » Oral Care Guidebook » Engineered Plaque Disclosing Tablets: The New Biofilm Standard <5% Dosage Error: Why Precision Tablets Are Replacing Liquids
You are here: Home » Blogs » Oral Care Guidebook » Engineered Plaque Disclosing Tablets: The New Biofilm Standard <5% Dosage Error: Why Precision Tablets Are Replacing LiquidsEngineered Plaque Disclosing Tablets: The New Biofilm Standard <5% Dosage Error: Why Precision Tablets Are Replacing Liquids
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-12-31 Origin: Site
Introduction: Visualization Is No Longer Optional
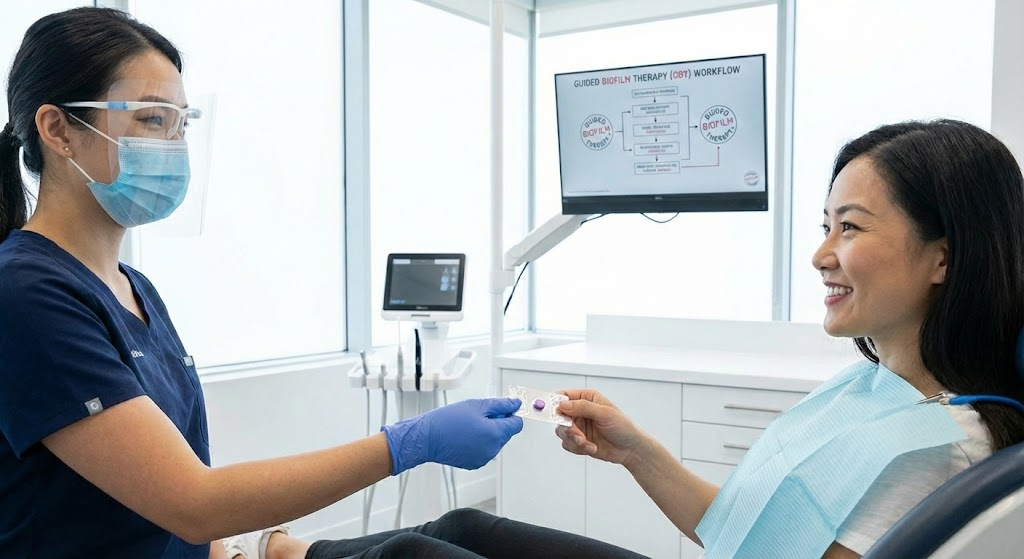
In modern preventive dentistry, plaque disclosing tablets for professional dental hygiene are no longer supplementary teaching aids. They have become a functional prerequisite for accurate biofilm assessment, patient communication, and risk-based preventive care.
As clinical frameworks such as Guided Biofilm Therapy (GBT) continue to reshape prophylaxis workflows, plaque must first be identified, classified, and explained before it is removed. Biofilm visualization is now the first diagnostic step, not an afterthought.
Despite this shift, a large portion of the global market still relies on legacy liquid plaque disclosing agents and pre-soaked swabs—formats developed decades ago for low-frequency use, long before modern infection control, dosing accuracy, and chairside efficiency became critical clinical concerns.
For professional oral care brands and OEM partners, the opportunity today is not to source another dye-based product.
It lies in engineering two-tone plaque disclosing tablets OEM solutions that align with contemporary diagnostics, hygiene standards, and real clinical workflows.Why the Shift from Liquid Plaque Disclosing Agents Is Becoming Inevitable
Liquid plaque disclosing agents were adopted primarily for manufacturing convenience, not because they were engineered for modern clinical environments. As dentistry has evolved, the limitations of these formats have become increasingly difficult to ignore.
Hygiene and Infection Control Limitations
Multi-use bottles and communal swabs introduce unavoidable hygiene risks. In both dental clinics and educational settings, repeated contact with applicators increases the likelihood of cross-contamination—directly conflicting with modern infection control in plaque visualization standards.
Single-dose tablets eliminate shared contact points, making them inherently more compatible with contemporary infection control protocols.
Inconsistent Dosing and Diagnostic Variability
Manual application methods—dripping liquid or transferring dye with cotton pellets—result in highly variable dosing. Drop size, angle, operator technique, and saliva flow all affect final dye distribution.
This variability directly undermines dosing accuracy in plaque disclosing agents, leading to inconsistent visualization and reduced diagnostic reliability.
Workflow Inefficiency and Poor Compliance
Liquid disclosing agents frequently stain sinks, gloves, skin, clothing, and instruments. This “mess factor” discourages routine use, particularly in high-throughput hygiene settings. Reduced usage ultimately weakens plaque visualization as a preventive diagnostic tool.
Dosing Accuracy: A Functional Requirement, Not a Feature
In professional diagnostics, dosing accuracy is not a cosmetic improvement—it is a functional requirement.
Liquid disclosing systems typically exhibit dosage deviations of ±30% or more, depending on application conditions. This margin of error is incompatible with standardized diagnostic protocols, especially when plaque visualization is used for clinical decision-making and patient education.
Engineered plaque disclosing tablets, by contrast, are pre-calibrated single-dose systems. Properly designed tablets achieve <5% dosage variation, enabling reproducible staining outcomes across patients, operators, and clinical environments.
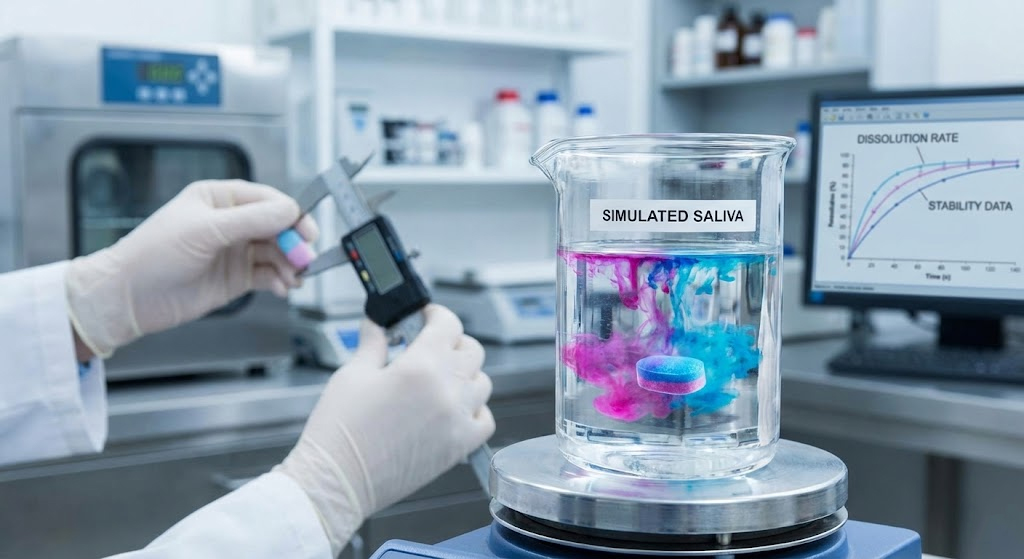
Laboratory Insights (R&D Note #402)
In simulated clinical testing, liquid-based plaque disclosing agents exhibited significant rheological variability. Due to uncontrolled flow behavior, approximately 35% of the liquid formulation migrated to non-target areas, including soft tissues and saliva-rich zones, resulting in reduced diagnostic precision.
By contrast, engineered plaque disclosing tablets achieve controlled disintegration rates, enabling 100% targeted dye release within intended biofilm contact zones.
Quantitative analysis shows that the effective utilization rate of active dyes increased by over 40% compared to conventional liquid disclosing agents under identical simulation conditions.
This improvement in utilization efficiency is the foundation of higher diagnostic precision.
![two tone plaque disclosing tablets two tone plaque disclosing tablets]()
Performance Comparison: Legacy Liquid vs. Engineered Tablets
Performance Metric Legacy Liquid Disclosing Agents Engineered Plaque Disclosing Tablets Clinical / OEM Significance Dosage Accuracy ±30% variation (application-dependent) <5% variation (pre-calibrated dose) Consistent diagnostics across clinics Active Enzyme Stability Unstable in aqueous systems; rapid degradation Stable in anhydrous solid form Enables functional enzyme-assisted diagnostics Overall Formula Stability Sensitive to moisture, oxygen, and light Dry-state protection with validated packaging Longer shelf life, lower failure risk Workflow Time ~45–60 seconds ~15 seconds Higher chairside efficiency Cross-Contamination Risk High (multi-use bottles, shared tools) Minimal (single-dose tablets) Aligns with infection control standards Diagnostic Consistency Operator-dependent Highly reproducible Supports GBT-aligned disclosure standards What Makes Two-Tone Plaque Disclosing the Emerging Clinical Standard
Single-color plaque disclosure answers only one question: Is plaque present?
Modern preventive dentistry requires a more advanced question: How mature and how risky is that plaque?Understanding Biofilm Maturity
Early-stage biofilm is loosely structured and relatively easy to remove. Mature biofilm is metabolically active and closely associated with caries progression and periodontal inflammation.
Single-color systems cannot differentiate between these stages.
Two-Tone Biofilm Risk Differentiation
Advanced biofilm risk detection tablets use balanced dye systems to distinguish plaque maturity:
Red or pink staining → newly formed, lower-risk plaque
Blue or purple staining → mature, high-risk biofilm
This differentiation supports clearer patient communication and aligns directly with biofilm disclosure standards for GBT protocols.
OEM Engineering Challenges Behind Tablet Performance
Plaque disclosing tablets may appear simple, but their performance depends on formulation science and mechanical engineering.
The Hardness vs. Disintegration Balance
Under-compressed tablets fracture during transport
Over-compressed tablets dissolve poorly and feel gritty
High-quality tablets balance logistics durability with rapid oral disintegration (typically 15–20 seconds).
At QIAOERNA Biotechnology, plaque disclosing tablets are engineered as oral solid dosage systems rather than confectionery products, ensuring reproducibility, stability, and clinical reliability.
Stability and Erythrosine-Free Formulation Considerations
High-grade disclosing dyes are sensitive to moisture and light. Without proper formulation control, discoloration and contrast loss can occur long before expiration.
Modern erythrosine-free plaque disclosing formulas—increasingly demanded in high-end US and EU markets—require:
Fully anhydrous formulation design
Accelerated stability testing
Packaging compatibility validation
A stable dye system for oral care diagnostic tablets must be engineered, not assumed.
One Engineered Platform, Multiple Clinical Applications
Engineered plaque disclosing tablets function as a modular diagnostic platform:
Pediatric Oral Care
Sugar-free plaque indicators for pediatric oral care, often xylitol-based, improve compliance and support educational use.
Orthodontic Care
Biofilm visualization tablets for orthodontic patients enhance foam penetration around brackets and wires, acting as effective orthodontic bracket plaque detection tools.
Professional Dental Hygiene
Rapid rinse-off, minimal residual staining, and accurate two-tone differentiation allow seamless integration into routine hygiene appointments.
![plaque disclosing tablets plaque disclosing tablets]()
Conclusion: Precision Is Becoming the New Competitive Standard
Plaque disclosing agents are no longer peripheral educational tools. They are evolving into front-line diagnostic instruments within modern preventive dentistry.
As preventive protocols raise expectations around biofilm assessment, the limitations of liquid disclosing systems—unstable actives, poor dosing accuracy, hygiene risks, and workflow inefficiency—have become structurally unacceptable.
Engineered plaque disclosing tablets represent a shift toward measurable precision, reproducibility, and clinically interpretable diagnostics.
In the high-end dental market, brands are no longer competing on price, but on measurable precision. A 25% increase in diagnostic accuracy is the bridge between a simple consumer product and a professional medical tool.
For oral care brands and OEM partners alike, the future of plaque disclosure will be defined not by dye sourcing, but by engineering systems that deliver consistent diagnostic outcomes, clinical trust, and long-term professional relevance.
Author: XiaoYing
Title: Chief R&D Engineer, QIAOERNA BiotechnologyRelated ProductsProduct Category
Other Links